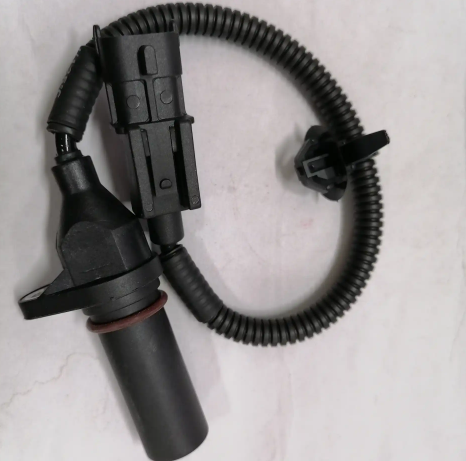
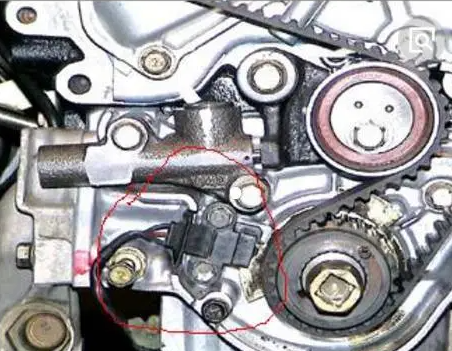
Polaris crank position sensor
What happens when the crank sensor goes bad?
Polaris ranger crank position sensor symptoms: When a crankshaft position sensor goes bad, it can lead to a variety of issues that affect the performance and reliability of the engine. Here are some common problems you might encounter:
- Difficulty Starting the Engine: The engine may crank but struggle to start, or it might not start at all.
- Stalling: The engine might suddenly stall while idling or at low speeds.
- Misfiring: You might experience misfires in one or more cylinders, leading to rough running.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light could illuminate, indicating a problem with the sensor. Diagnostic trouble codes related to the crankshaft sensor may be stored.
- Poor Acceleration: There might be a noticeable lag or hesitation when you try to accelerate.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The engine might consume more fuel than usual, leading to lower fuel economy.
- Vibrations and Rough Running: The engine could run roughly or vibrate more than normal.
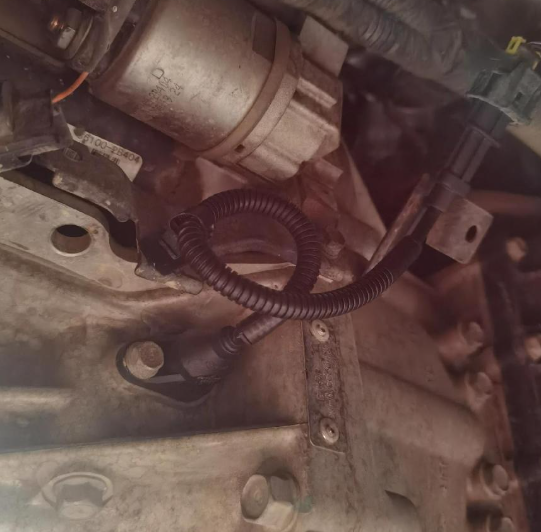

Because the crankshaft position sensor provides critical information about the engine’s position and speed, a failing sensor can cause significant disruptions to engine management and timing. Polaris sportsman 570 crank position sensor
How do you reset a crankshaft position sensor?
Resetting a crankshaft position sensor usually involves performing a relearn procedure to ensure the engine control module (ECM) recognizes the new sensor correctly. Here’s how you can do it:
Steps for Relearn Procedure:
- Disconnect the Battery: Turn off the ignition and disconnect the negative battery cable. Wait for about 10-15 minutes to reset the ECM.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it idle. The ECM will start to learn the new sensor’s position automatically.
- Driving Cycle:
- Let the engine warm up to its normal operating temperature.
- Drive the vehicle at various speeds and loads. Try to include highway driving, city driving, and idling periods to provide a complete range of operating conditions.
- Check for Errors: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any error codes. If everything is working correctly, there should be no codes related to the crankshaft position sensor.
- Clear Codes (if necessary): If the check engine light remains on or there are any error codes, use the OBD-II scanner to clear them. Sometimes the ECM needs a bit more time to adapt to the new sensor.
How do you test if a crank sensor is working?
Polaris crank position sensor test: Testing a crankshaft position sensor involves checking its electrical signals to ensure it’s functioning correctly. Here are a few steps you can follow to test a crank sensor:
Tools and Materials Needed:
- Multimeter (digital or analog)
- OBD-II scanner (optional, for reading diagnostic trouble codes)
- Repair manual specific to your vehicle (for reference)
Steps:
- Safety First: Ensure the vehicle is turned off and the key is removed from the ignition.
- Locate the Sensor: Find the crankshaft position sensor on your vehicle. Refer to your repair manual for the exact location.
- Inspect the Sensor and Wiring: Visually inspect the sensor and its wiring for any obvious signs of damage, such as frayed wires or loose connections.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Unplug the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Test the Resistance:
- Set your multimeter to the resistance (Ohms) setting.
- Place the multimeter probes on the sensor terminals.
- Check the resistance reading against the specifications in your repair manual. A typical reading might be between 200-1,200 Ohms, but it varies by sensor and vehicle.
- Test for Voltage Signal:
- Reconnect the sensor to the vehicle’s wiring harness.
- Set your multimeter to the voltage (Volts) setting.
- Connect the multimeter’s positive probe to the signal wire of the sensor and the negative probe to a ground point.
- Have someone crank the engine while you observe the multimeter reading. You should see a fluctuating voltage signal, which indicates the sensor is sending data to the engine control module (ECM).
- Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (Optional): Use an OBD-II scanner to read any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the crankshaft position sensor. Common codes are P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Malfunction) and P0339 (Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Intermittent).