2008 dodge avenger camshaft position sensor location
How many camshaft sensors does a 2008 Dodge Avenger have?
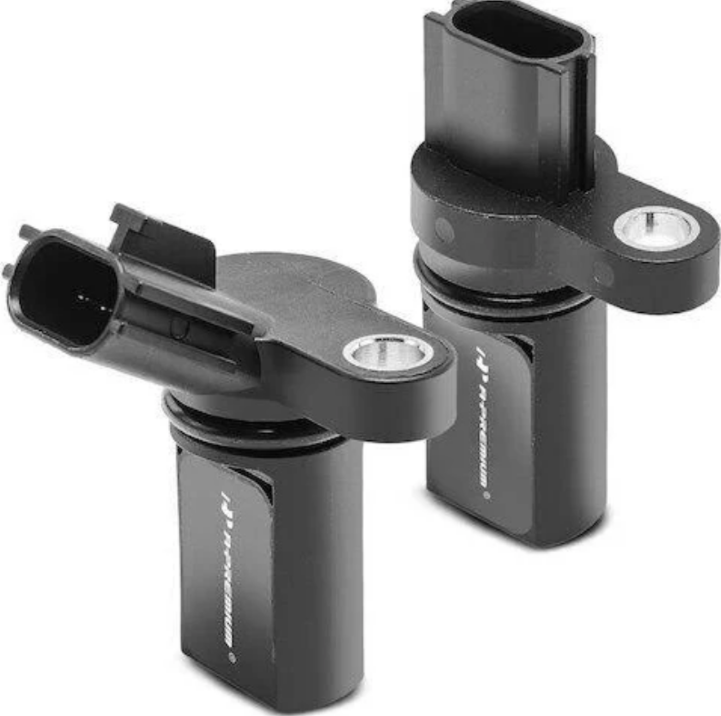
A 2008 Dodge Avenger typically has two camshaft position sensors: one for the intake camshaft and one for the exhaust camshaft.
Where is the camshaft position sensor located?
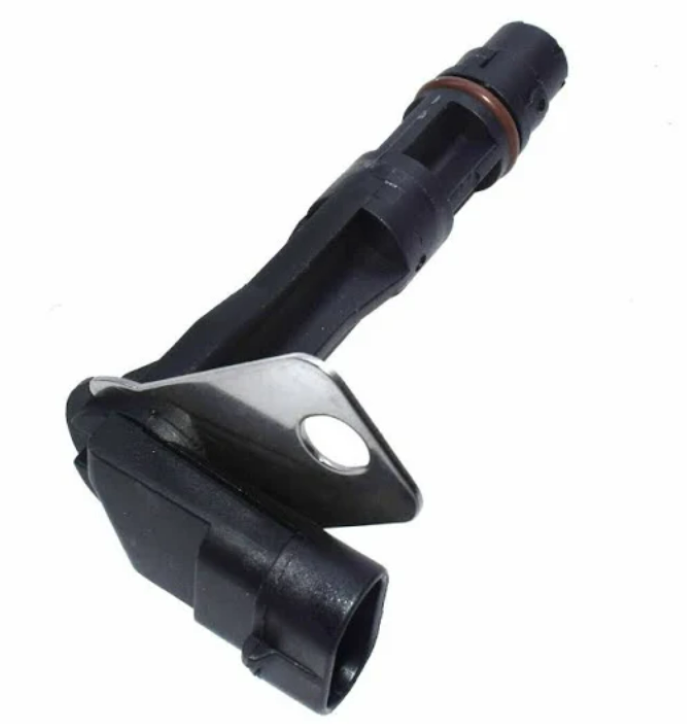
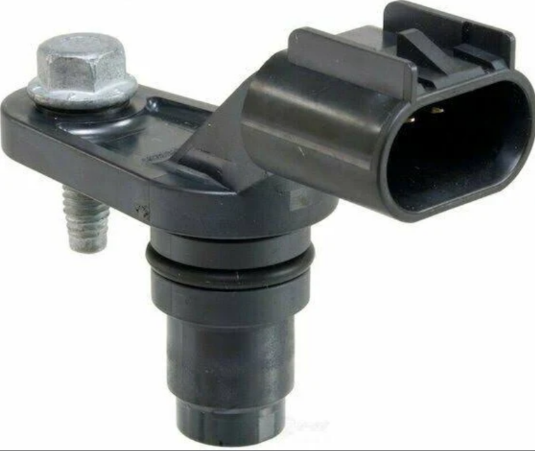
2008 dodge avenger cam sensor location: The location of the camshaft position sensor can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model. However, for a 2008 Dodge Avenger, the camshaft position sensors are generally found in the following locations:
- 2.4L Engine: The sensors are usually located on the sides of the cylinder head, near the camshaft itself.(2008 dodge avenger 2.4 camshaft position sensor location)
- 3.5L V6 Engine: The sensors are typically located under the alternator, attached to the timing cover.(2008 dodge avenger 3.5 camshaft position sensor location)

What happens when the camshaft sensor goes bad?
When a 2012 dodge avenger camshaft position sensor goes bad, it can cause several engine performance issues due to the loss of critical data used by the engine control module (ECM). Here’s what you might experience:
- Difficulty Starting: The engine may crank but struggle to start, or it might not start at all.
- Engine Stalling: The engine might suddenly stall while idling or at low speeds.
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle roughly, leading to vibrations and shaking.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light will likely come on, indicating a problem with the sensor.
- Poor Acceleration: You might notice hesitation or a lack of power when you try to accelerate.
- Misfiring: The engine may misfire, causing rough running and loss of power.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The engine might consume more fuel than usual, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Engine Vibrations: The engine could run roughly or vibrate more than normal.

What is the code P0016 on a Dodge Avenger?
The code P0016 on a Dodge Avenger indicates a “Camshaft Position – Crankshaft Position Correlation” issue. This means that the camshaft and crankshaft positions are not synchronized correctly, which can affect the engine’s performance.
Common symptoms of this code include:
- Engine misfires or rough idling
- Engine stalling or hesitation during acceleration
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Check Engine Light illuminated on the dashboard