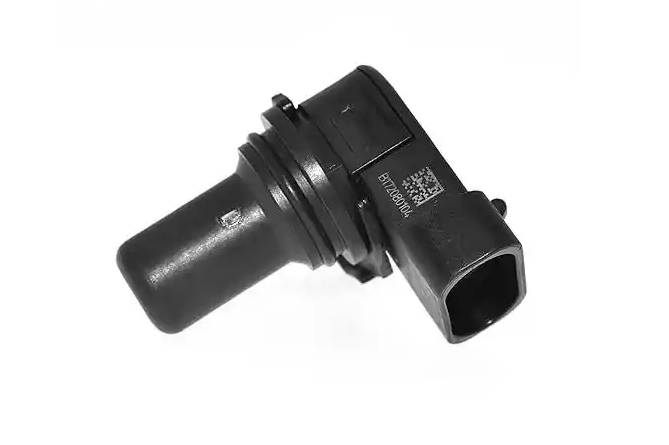
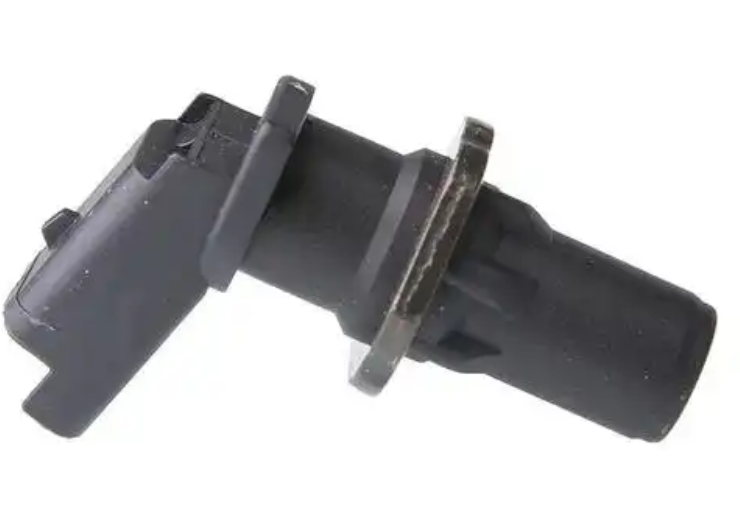
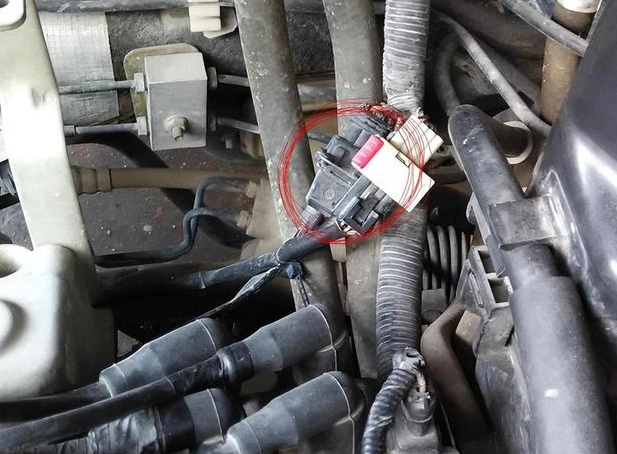
Delphi Engine Crankshaft Position Sensor SS12018
What are the 7 symptoms of a bad crankshaft position sensor?
A bad Delphi crankshaft position sensor can cause a number of noticeable symptoms on this vehicle. Here are seven common symptoms::
- Engine Misfires: The engine may misfire or run roughly due to incorrect data being sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Stalling: The engine might stall unexpectedly, which can occur both at idle and while driving.
- Starting Problems: You might experience difficulty starting the vehicle, or it may take longer than usual to start.
- Check Engine Light: The “Check Engine” light may illuminate on your dashboard.
- Poor Acceleration: You may notice a lack of power or poor acceleration while driving.
- Irregular Idling: The engine may idle inconsistently or roughly.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The engine might consume more fuel than usual due to improper ignition timing and fuel mixture.
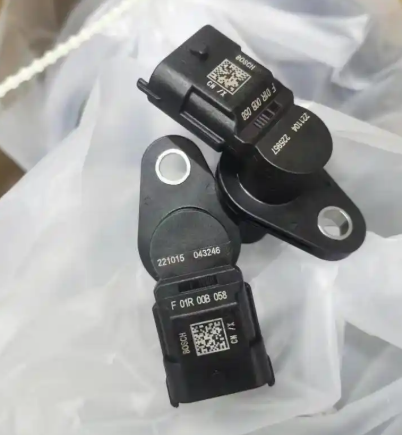

What code will a bad crankshaft sensor throw?
A bad Delphi engine crankshaft position sensor typically triggers the P0335 code, which stands for “Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction”. This code indicates that the engine control unit (ECU) is not receiving proper signals from the crankshaft position sensor.
Is a TDC sensor the same as a crankshaft position sensor?
The TDC (top dead center) sensor and the crankshaft position sensor have similar functions, but they are not exactly the same. There are the following differences:
Crankshaft Position Sensor:
- Function: Monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft.
- Purpose: Provides data to the engine control unit (ECU) for controlling ignition timing and fuel injection.
TDC Sensor:
- Function: Specifically monitors the crankshaft’s position when the piston is at the top of its stroke (Top Dead Center).
- Purpose: Used in some engines to precisely determine the piston’s TDC position for accurate ignition timing and fuel injection.
Key Differences:
- Scope: The crankshaft position sensor provides continuous data about the crankshaft’s position and speed throughout its rotation, while the TDC sensor focuses on the top dead center position.
- Usage: Some engines use both sensors for more accurate engine management, while others rely solely on the crankshaft position sensor.